EV Charging Types Explained-Detailed Comparison of EV Charging Types
EV Charging Types
What are the different types of EV charging, and what are the differences between them?
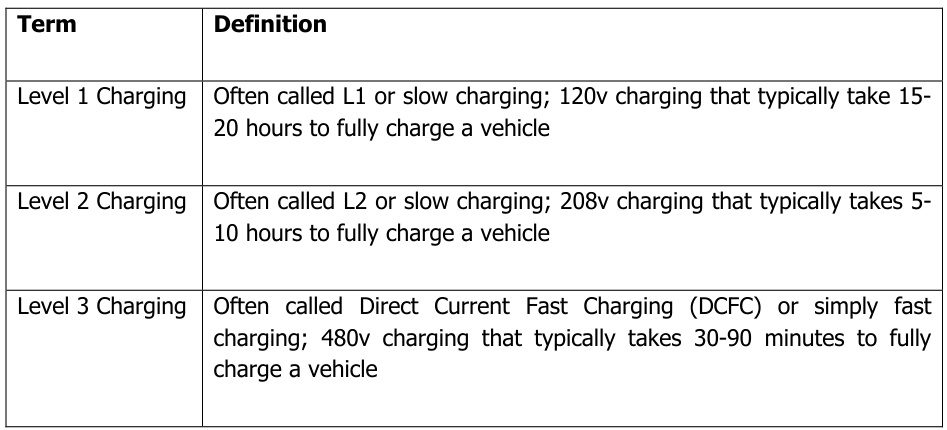
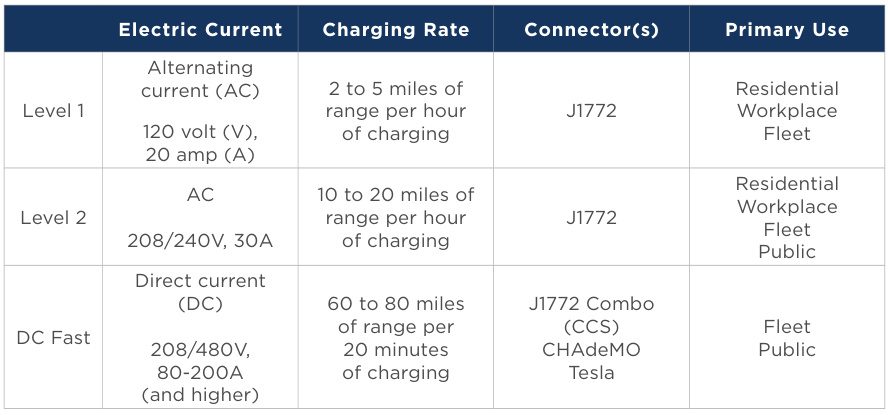
1. Level 1 (Slow/Basic Charging)
Voltage/Power: 120V AC, ≤3.7kW
Charging Time: 8–20 hours for a full charge (varies by battery capacity)
Use Cases: Standard household outlets, overnight charging
Features: Low cost, minimal battery degradation, but extremely slow
Connector: Type 1 (J1772) or standard three-prong household plug
2. Level 2 (Medium-Speed/Destination Charging)
Voltage/Power: 208–240V AC, 7–22kW
Charging Time: 4–10 hours for a full charge
Use Cases: Home charging stations, workplaces, destinations (malls/hotels)
Features: Balances speed and battery longevity; most widely used
Connector: Type 2 (Mennekes) or Type 1 (J1772)
3. DC Fast Charging (DCFC/Rapid Charging)
Voltage/Power: 480V DC, 50–180kW (common); Ultra-Fast Charging: 180–350kW
Charging Time: 30–90 minutes to reach 80% SOC (avoids full charge to protect battery)
Use Cases: Highway rest stops, emergency top-ups, long-distance travel
Features: Fastest charging speed, but frequent use may accelerate battery degradation
Connectors:
- CHAdeMO (Japanese vehicles)
- CCS (Combo, European/American vehicles)
- Tesla Supercharger (proprietary connector)
EV Charging Connector
The type of connectors to recharge electric vehicles (BEVs) varies from the regulations of the country of marketing, individual manufacturers, and the type of charging.
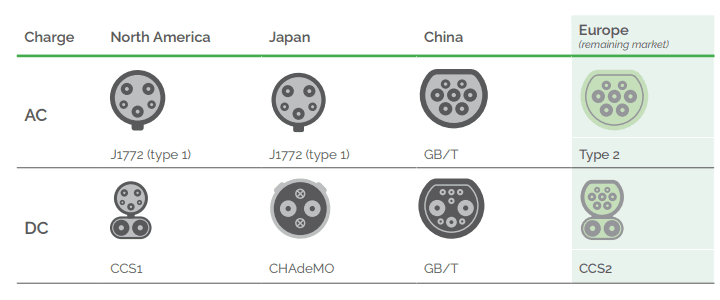
| Connector Type | Applicable Charging Methods | Main regions/vehicle models | Features |
| Type 1(J1772) | AC Level 1/2 | North America and Japan models | AC power only |
| Type 2 (Mennekes) | AC Level 2 | European mainstream | Compatible with certain DC fast charging systems |
| CCS (Combo) | DC Fast Charging | European and American cars (such as Volkswagen and BMW) | Integrated Type 1/2 interface expansion |
| CHAdeMO | DC Fast Charging | Japanese car (such as Nissan) | High power compatibility |
| Tesla-specific | DC Supercharging | Tesla Lineup | Exclusive supercharging network |
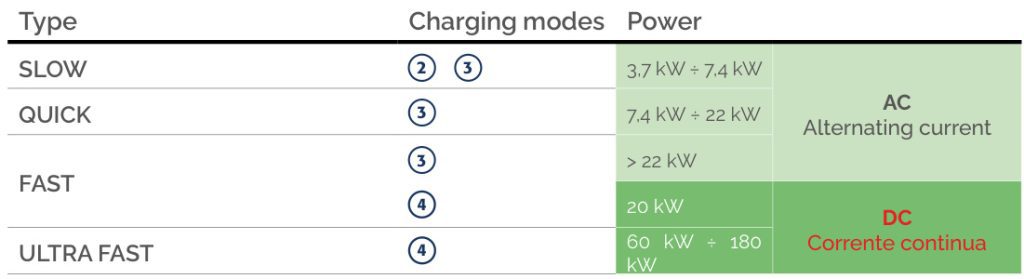
EV Charging Mode
What does EV mode mean?What is the difference between CCS Type 1 and Type 2?What is mode 4 EV charging?
①Mode 1 – Home socket and extension cord in AC
Mode 1 is the direct connection of the electric medium to household outlets (230/400VAC).
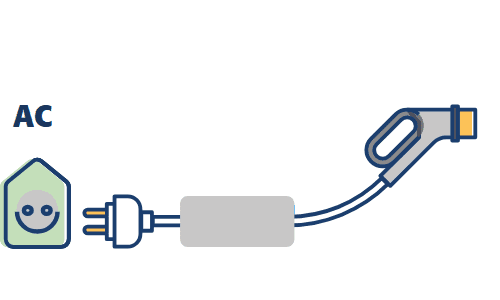
②Mode 1 – Mode 2 – Home socket with AC control
Mode 2 is the direct connection of the electric medium to household or industrial outlets (230/400VAC) through a cable that integrates control electronics between the vehicle and the power grid. It is therefore a portable charging station for use in private areas only.
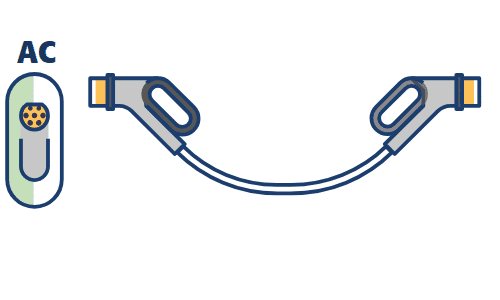
③Mode 3 – Fixed AC charging station with removable cable
These are fixed charging stations (WallBox) in 230/400 V alternating current specifically for electric vehicle charging that provides appropriate fixed control contacts. The sockets and connectors adopted for Mode 3 in Europe and other countries are those of Type 2, according to EN 62196-2.
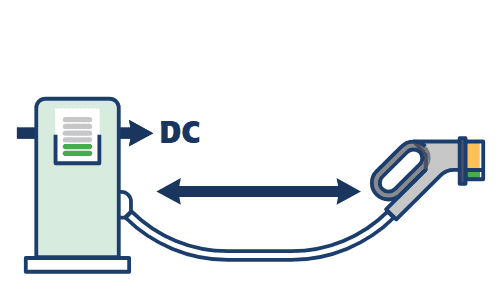
④Mode 4 – Fixed DC charging station
This charging method consists of connecting the vehicle to DC connectors incorporating, control and protection functions and the Charger regulating the charging current delivered. Dedicated method for ‘Fast and Ultra Fast charge” involving power above 20 kW/ DC up to the maximum powers of the A1 9000 line.
If you are interested in Chinese electric vehicle brands, please click here to view:Chinese EV>>>





